Code Optimization-
Code Optimization is an approach to enhance the performance of the code.
The process of code optimization involves-
- Eliminating the unwanted code lines
- Rearranging the statements of the code
Advantages-
The optimized code has the following advantages-
- Optimized code has faster execution speed.
- Optimized code utilizes the memory efficiently.
- Optimized code gives better performance.
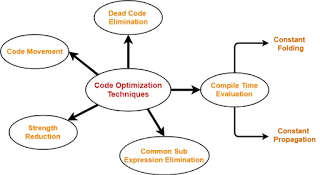
Code Optimization Techniques-
Important code optimization techniques are-
- Compile Time Evaluation
- Common sub-expression elimination
- Dead Code Elimination
- Code Movement
- Strength Reduction
1. Compile Time Evaluation-
Two techniques that falls under compile time evaluation are-
A) Constant Folding-
In this technique,
- As the name suggests, it involves folding the constants.
- The expressions that contain the operands having constant values at compile time are evaluated.
- Those expressions are then replaced with their respective results.
Example-
Circumference of Circle = (22/7) x Diameter
Here,
- This technique evaluates the expression 22/7 at compile time.
- The expression is then replaced with its result 3.14.
- This saves the time at run time.
B) Constant Propagation-
In this technique,
- If some variable has been assigned some constant value, then it replaces that variable with its constant value in the further program during compilation.
- The condition is that the value of variable must not get alter in between.
Example-
pi = 3.14
radius = 10
Area of circle = pi x radius x radius
Here,
- This technique substitutes the value of variables ‘pi’ and ‘radius’ at compile time.
- It then evaluates the expression 3.14 x 10 x 10.
- The expression is then replaced with its result 314.
- This saves the time at run time.
2. Common Sub-Expression Elimination-
The expression that has been already computed before and appears again in the code for computation
is called as Common Sub-Expression.
In this technique,
- As the name suggests, it involves eliminating the common sub expressions.
- The redundant expressions are eliminated to avoid their re-computation.
- The already computed result is used in the further program when required.
Example-
Code Before Optimization Code After Optimization
S1 = 4 x i S1 = 4 x i
S2 = a[S1] S2 = a[S1]
S3 = 4 x j S3 = 4 x j
S4 = 4 x i // Redundant Expression S5 = n
S5 = n
S6 = b[S4] + S5 S6 = b[S4] + S5
3. Code Movement-
In this technique,
- As the name suggests, it involves movement of the code.
- The code present inside the loop is moved out if it does not matter whether it is present inside or outside.
- Such a code unnecessarily gets execute again and again with each iteration of the loop.
- This leads to the wastage of time at run time.
Example-
Code Before Optimization Code After Optimization
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++) x = y + z ;
{ for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++)
x = y + z ; {
a[j] = 6 x j; a[j] = 6 x j;
} }
4. Dead Code Elimination-
In this technique,
- As the name suggests, it involves eliminating the dead code.
- The statements of the code which either never executes or are unreachable or their output is never used are eliminated.
Example-
Code Before Optimization Code After Optimization
if (i == 1) i = 0
{
a = x + 5 ;
}
i = 0 ;
5. Strength Reduction-
In this technique,
- As the name suggests, it involves reducing the strength of expressions.
- This technique replaces the expensive and costly operators with the simple and cheaper ones.
Example-
Code Before Optimization Code After Optimization
B = A x 2 B = A + A
Here,
- The expression “A x 2” is replaced with the expression “A + A”.
- This is because the cost of multiplication operator is higher than that of addition operator.
Comments