Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article onTypes of Grammarin Automata.
On the basis of number of derivation trees, grammars are classified as-
- Ambiguous Grammar
- Unambiguous Grammar
1. Ambiguous Grammar-
A grammar is said to ambiguous if for any string generated by it, it produces more than one-
- Parse tree
- Or derivation tree
- Or syntax tree
- Or leftmost derivation
- Or rightmost derivation
Example-
Consider the following grammar-
E → E + E / E x E / id
Ambiguous Grammar
This grammar is an example of ambiguous grammar.
Any of the following reasons can be stated to prove the grammar ambiguous-
Reason-01:
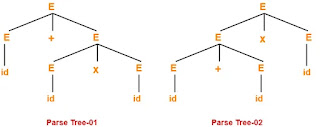
Let us consider a string w generated by the grammar-
w = id + id x id
Now, let us draw the parse trees for this string w.
Since two parse trees exist for string w, therefore the grammar is ambiguous.
Reason-02:
Let us consider a string w generated by the grammar-
w = id + id x id
Now, let us draw the syntax trees for this string w.
Since two syntax trees exist for string w, therefore the grammar is ambiguous.
Reason-03:
Let us consider a string w generated by the grammar-
w = id + id x id
Now, let us write the leftmost derivations for this string w.
Since two rightmost derivations exist for string w, therefore the grammar is ambiguous.
2. Unambiguous Grammar-
A grammar is said to unambiguous if for every string generated by it, it produces exactly one-
- Parse tree
- Or derivation tree
- Or syntax tree
- Or leftmost derivation
- Or rightmost derivation
Example-
Consider the following grammar-
E → E + T / T
T → T x F / F
F → id
Unambiguous Grammar
This grammar is an example of unambiguous grammar.



Comments